Introduction
Blockchain basics explain how this digital ledger securely records transactions across multiple computers. It eliminates intermediaries, such as banks, ensuring transparency, security, and efficiency. In Saudi Arabia, blockchain technology supports Vision 2030, helping businesses simplify processes, strengthen security, and drive innovation. Companies can explore blockchain strategy consulting to build customized blockchain solutions.
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain stores information in blocks connected through cryptographic hashes, making the data tamper-proof. Each block records transactions, which are verified and secured by a distributed network of computers called nodes. As a result, blockchain removes the need for central authorities while ensuring trust and security.
Many businesses in Saudi Arabia are already leveraging custom blockchain development to boost efficiency and reliability. For more insights, visit Investopedia’s blockchain guide.
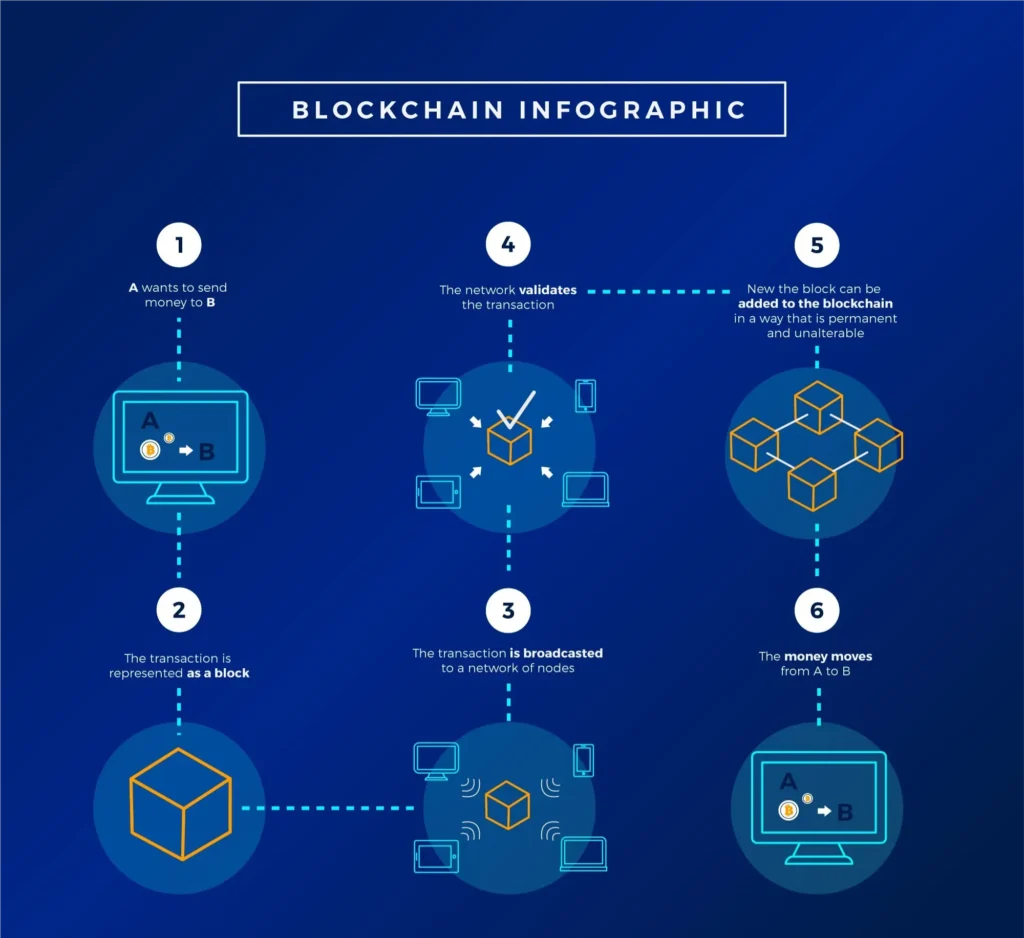
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain basics can be understood through these simple steps.
- Transaction Initiation: A user starts a transaction, such as sending cryptocurrency or storing records.
- Block Creation: The transaction details are saved inside a block of data.
- Verification: Network participants, called nodes, validate the block using Proof of Work or Proof of Stake mechanisms.
- Block Linking: Once verified, the block joins the chain, creating a permanent record.
- Immutability: The data cannot be altered without changing the entire chain, ensuring integrity.
Because this process prevents tampering, blockchain works well for industries needing security and traceability. Learn more through Coinbase’s blockchain guide.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralization – Data is shared across a network, removing single points of failure.
- Transparency – Publicly recorded transactions build trust and accountability.
- Security – Cryptographic encryption protects against fraud and data breaches.
- Immutability – Data becomes permanent, ensuring accuracy and reliability.
- Smart Contracts – Automated agreements run based on pre-set rules, reducing errors.
Explore how businesses can adopt smart contract development to streamline operations.
Types of Blockchains
Blockchain basics include three types of blockchain networks:
- Public Blockchains: Open to everyone and widely used for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Private Blockchains: Restricted to authorized users, making them ideal for enterprises and financial services.
- Consortium Blockchains: Controlled by multiple organizations for shared governance, especially in supply chains.
Discover more applications on IBM’s blockchain solutions page.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain basics cover several applications across industries.
- Financial Services: Allows peer-to-peer payments and reduces transaction costs.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracks goods transparently from production to delivery.
- Healthcare: Secures patient data and improves privacy.
- Real Estate: Simplifies property transactions through smart contracts.
- Gaming and NFTs: Enables digital ownership and tokenized rewards.
Explore tokenomics strategy planning to see how blockchain improves compliance and efficiency.
Challenges to Consider
While blockchain basics offer many advantages, businesses should consider the following challenges.
- Scalability Issues: High transaction volumes sometimes slow down public blockchains.
- Regulatory Compliance: Companies must keep up with evolving blockchain laws in Saudi Arabia.
- Implementation Costs: Setting up blockchain systems often requires investment and expertise.
To address these challenges, businesses can consult enterprise blockchain experts for tailored solutions.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is transforming industries through security, automation, and transparency. Businesses in Saudi Arabia are already adopting blockchain basics to align with Vision 2030 and promote growth.
If you’re ready to integrate blockchain into your operations, explore blockchain strategy consulting and unlock new opportunities for innovation.
