What is Blockchain? A Beginner’s Guide to Decentralized Technology
Blockchain technology is transforming industries by enabling secure, decentralized, and transparent systems. It powers cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi), and smart contracts, becoming a foundational element of modern digital systems. But what exactly is it, and how does it work? This article explores concepts, features, and applications, particularly its relevance to Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain refers to a distributed digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in a secure and transparent way. Unlike centralized databases, it operates without intermediaries, relying instead on a peer-to-peer network. Transactions are grouped into blocks, validated, and added to a chain in chronological order, ensuring immutability and trust.
Core Features
- Decentralization – The network operates without a single authority, enhancing security and reducing reliance on central control.
- Transparency – Every transaction is visible and can be verified by network participants, ensuring accountability.
- Security – Cryptographic encryption prevents tampering and unauthorized access to stored data.
- Immutability – Once a block is added, it cannot be altered, providing a permanent record of transactions.
- Smart Contracts – Automated programs enforce agreements without intermediaries. Learn more about Smart Contract Development.
How Does Blockchain Work?
It operates through a sequence of steps:
- Transaction Initiation – Users submit transactions, which are digitally signed for authenticity.
- Block Creation – The transactions are grouped into a block and sent to the network.
- Validation Process – Nodes validate the block using consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Adding to the Chain – After validation, the block is added to the chain, creating a permanent record.
- Distributed Ledger Update – All network participants receive an updated copy of the ledger, confirming the transaction.
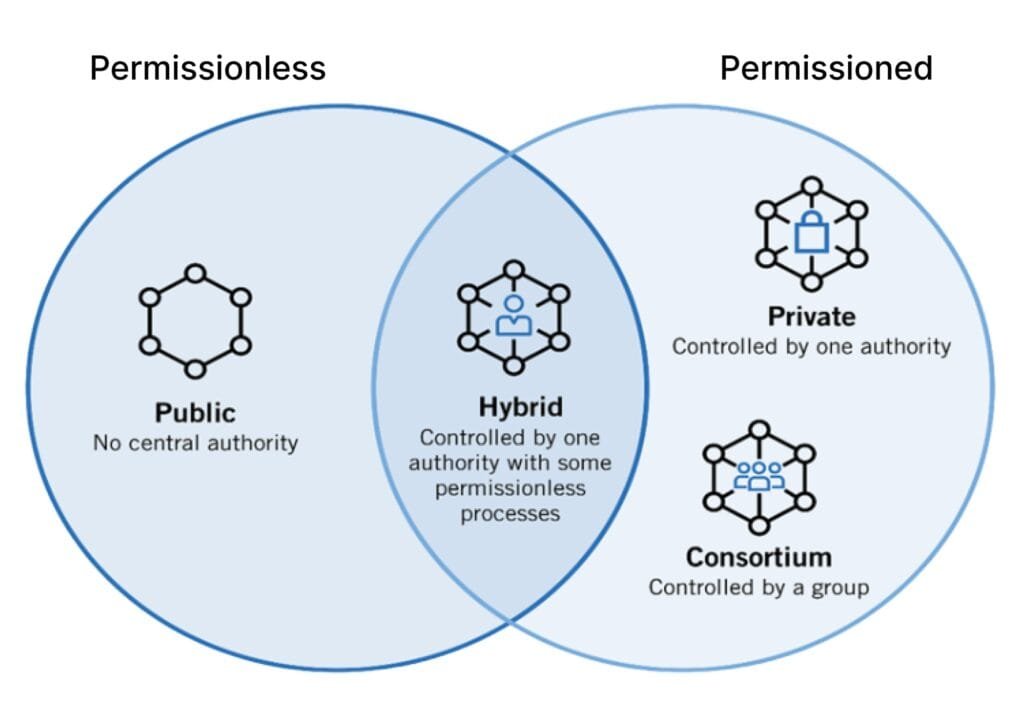
Types of Blockchain Networks
- Public Networks – Open systems, including Bitcoin and Ethereum, where anyone can participate.
- Private Networks – Restricted systems designed for enterprise use, ensuring secure data sharing. Learn more about Private Blockchain Consulting.
- Consortium Models – Multi-organization governance for collaborative applications.
- Hybrid Solutions – Combines public transparency with private control for flexibility.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
The technology has already impacted various industries.
- Cryptocurrencies – It facilitates decentralized, peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries.
- Supply Chain Management – Businesses can track products in real time, reducing fraud.
- Healthcare – Secure sharing of medical records improves efficiency and data protection.
- Voting Systems – Ensures transparent and tamper-proof election processes.
- Asset Tokenization – Allows fractional ownership of assets like real estate and art. Learn more about Tokenomics Strategy and Planning.
- Identity Management – Provides secure digital identities to prevent fraud.
Why Blockchain Matters for Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is actively implementing blockchain as part of Vision 2030 to advance digital transformation. The technology supports financial systems, supply chains, and governance reforms.
Benefits for Saudi Arabia
- Financial Inclusion – Reduces costs and improves access to digital payments.
- Innovation in Enterprises – Encourages growth through enterprise blockchain consulting.
- Transparency – Lowers fraud risks and enhances accountability.
- Smart Cities – Drives urban development and IoT-enabled ecosystems.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Although it offers significant advantages, challenges remain:
- Scalability – Managing high transaction volumes efficiently.
- Energy Usage – Reducing resource-intensive mining processes.
- Regulatory Clarity – Establishing frameworks for adoption.
- Interoperability – Improving compatibility between blockchain systems.
Advances in Layer 2 scaling and green energy solutions are already addressing these challenges.

Conclusion
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology reshaping industries with its decentralized, transparent, and secure framework. It supports digital payments, smart contracts, and secure data sharing, offering businesses efficiency and innovation. In Saudi Arabia, blockchain aligns with Vision 2030 to create a modern, transparent digital economy.